Are you aware that Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) servers are a prime target for cybercriminals? A recent study by IBM found that RDP attacks were responsible for 20% of all data breaches in 2022. That’s because RDP servers provide a convenient way for attackers to gain remote access to networks and steal data.
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) servers play a crucial role in facilitating remote work for businesses. Yet, without robust security measures, these servers can become significant vulnerabilities. To safeguard against potential threats, it’s imperative to adopt a systematic approach. This article delves into essential best practices and security tools, offering a step-by-step guide to fortify RDP servers and enhance overall security.
Risks and Vulnerabilities of RDP Servers
In the world of cybersecurity, Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) servers stand out as a prime target for malicious actors. These servers offer a convenient gateway for remote access to systems and networks, making them a hotspot for cyber threats. Recent data from Verizon reveals that RDP accounted for a staggering 17% of all data breaches in 2022, solidifying its position as the most common attack vector.
Let’s delve into the specific vulnerabilities that make RDP servers susceptible to compromise:
- Weak passwords and authentication: RDP servers are often targeted by brute-force attacks, where attackers attempt to guess login credentials using automated tools. Weak passwords and outdated authentication protocols can make RDP servers more susceptible to these attacks.
- Unpatched software: Vulnerabilities in RDP server software and the underlying operating system can be exploited to gain unauthorized access to systems. It is important to keep RDP server software and operating systems up to date with the latest security patches.
- Misconfigurations: Misconfigured RDP settings, such as enabling remote access from untrusted networks or using weak encryption protocols, can create security vulnerabilities.
A breach of an RDP server can have a devastating impact on organizations, leading to:
- Data theft: Attackers may steal sensitive data, such as customer records, financial information, and intellectual property.
- Ransomware attacks: Attackers may deploy ransomware to encrypt data and demand a ransom payment for its decryption.
- System disruption: Attackers may disrupt system operations, causing downtime and productivity losses.
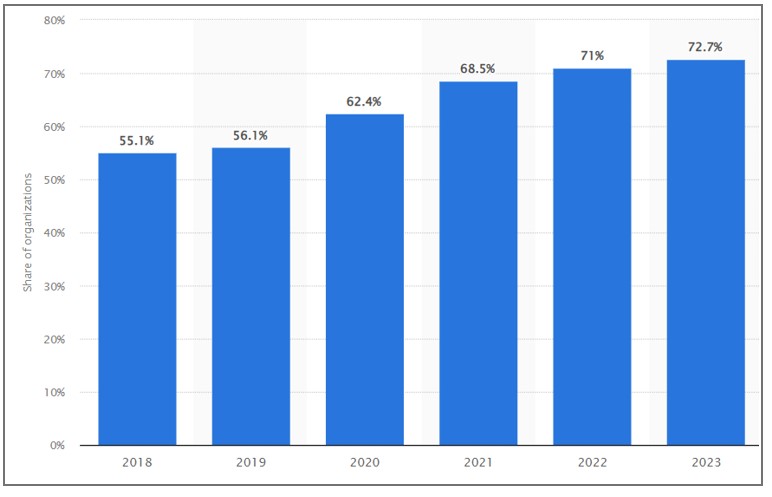
Annual share of organizations affected by ransomware attacks worldwide from 2018 to 2023 | source- statista.com
To mitigate these risks effectively, organizations must adopt a proactive approach to RDP server security, implementing robust security measures and best practices to fortify their defenses.
Step-by-Step Guide to Securing an RDP Server
Securing an RDP server requires a holistic approach, encompassing various aspects of server configuration, access control, and encryption. By following the step-by-step guide below, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and enhance the overall security posture of their RDP servers:
Step 1: Implement Strong Authentication Mechanisms:
One of the fundamental steps in securing an RDP server is to enforce strong authentication mechanisms, such as complex passwords or passphrase policies and multi-factor authentication (MFA). By mandating strong, unique passwords and incorporating MFA, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access to the RDP server. According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), “MFA is one of the most effective ways to protect against a wide range of cyberattacks”.
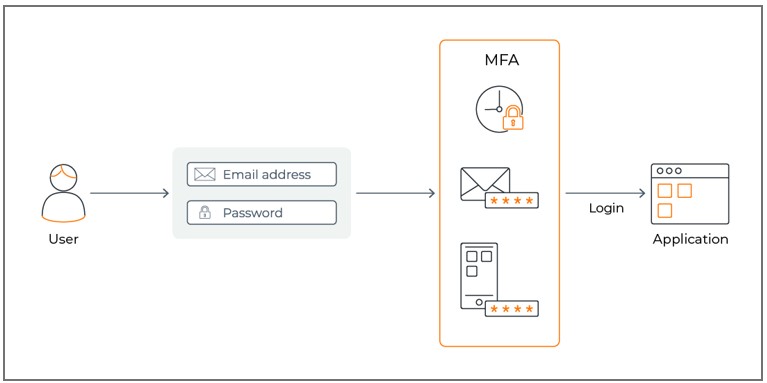
Step 2: Apply Security Updates and Patches:
In 2022, Microsoft patched over 1,200 vulnerabilities in its Windows operating system.Many of these vulnerabilities could have been exploited by attackers to gain access to RDP servers and other systems. Regularly updating the RDP server software and the underlying operating system is crucial in addressing known vulnerabilities and safeguarding the server against exploit attempts. Organizations should establish a patch management process to ensure timely deployment of security updates, minimizing the window of exposure to potential threats.
Step 3: Change the Default Port:
By default, RDP uses port 3389. Changing this port to a non-standard one can help prevent automated attacks that target common ports. Choose a port that is not well-known and has not been assigned to other services. Remember to update your firewall settings to allow traffic on the new port.
Step 4: Configure Network Level Authentication (NLA):
Enabling NLA on the RDP server adds an extra layer of security by requiring authentication before a remote session is established. This helps in mitigating the risk of unauthorized access and strengthens the overall security posture of the server.
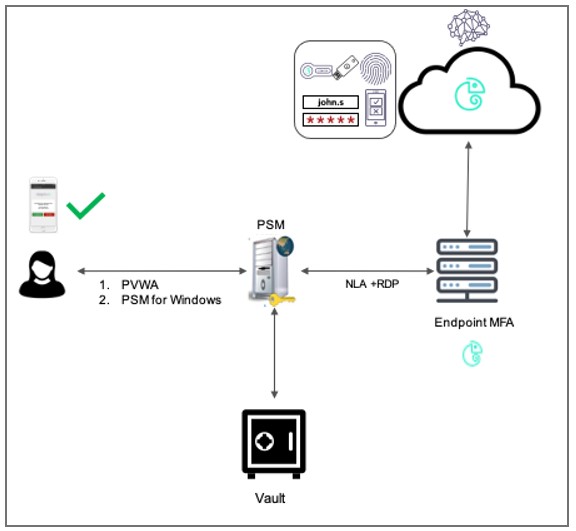
Step 5: Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) for Remote Access:
Consider using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) for remote access to your RDP server. A VPN encrypts the connection between the user’s device and the server, making it more difficult for attackers to intercept sensitive information. Only users with valid VPN credentials should be allowed to connect to the network. According to a recent study by PCMatic, 43% of remote workers use a VPN. This suggests that VPNs are how much popular and effective way to secure remote access.
Step 6: Restrict User Access and Permissions:
Implementing the principle of least privilege is essential in controlling user access to the RDP server. By assigning permissions based on specific job roles and responsibilities, organizations can limit the potential impact of unauthorized access and minimize the risk of privilege escalation within the server environment.

Step 7: Enable RDP Encryption:
According to Microsoft, “Encrypting RDP traffic is an important step in securing your RDP servers”. Utilizing strong encryption protocols, such as SSL/TLS, for RDP connections is critical in protecting data confidentiality and integrity during remote sessions.
By enforcing encryption, organizations can mitigate the risk of eavesdropping and unauthorized interception of sensitive information transmitted over RDP connections.
Step 8: Audit and Monitor RDP Server Access:
Implementing comprehensive logging and monitoring mechanisms allows organizations to track and analyze RDP server access, facilitating the detection of anomalous behavior and potential security incidents. By maintaining detailed audit trails, organizations can enhance their ability to respond to security threats effectively.
By following these step-by-step recommendations, organizations can strengthen the security of their RDP servers and mitigate the inherent risks and vulnerabilities associated with remote access and control.
Best Practices for RDP Server Security
In addition to the specific steps outlined in the previous section, there are several overarching best practices that organizations should adhere to to enhance the overall security of their RDP servers. These best practices encompass a holistic approach to RDP server security, addressing various aspects of configuration, access control, and monitoring.
- Regular Security Assessments and Vulnerability Scans: Conducting periodic security assessments and vulnerability scans of the RDP server environment is essential in identifying potential weaknesses and addressing them proactively. By leveraging security assessment tools and techniques, organizations can gain insights into the security posture of their RDP servers and take remedial actions to mitigate vulnerabilities.
- Establish Access Control Policies: Formulating and enforcing access control policies that define user privileges, authentication requirements, and session management guidelines is vital in maintaining the security of RDP servers. Organizations should delineate clear access control policies and procedures to govern remote access to critical systems and data.
- Implement Network Segmentation: Segregating RDP server traffic from other network segments can help in containing potential security breaches and limiting the impact of unauthorized access. By implementing network segmentation and access controls, organizations can reduce the attack surface and fortify the overall resilience of their network infrastructure.
- Regular Security Awareness Training: Educating employees and system administrators about the best practices for RDP server security and the potential risks associated with remote access is crucial in fostering a security-conscious culture within the organization. By promoting security awareness and training, organizations can empower their workforce to contribute to the overall security posture.
- Incident Response and Contingency Planning: Developing robust incident response and contingency plans specific to RDP server security incidents is essential in preparing for potential security breaches. Organizations should define clear protocols for responding to security incidents and establish contingency measures to mitigate the impact of breaches effectively.
By integrating these best practices into their overall security strategy, organizations can elevate the resilience of their RDP servers and fortify their defenses against a wide range of cyber threats.
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication for RDP
Multi-factor authentication (MFA), also known as two-factor authentication (2FA), adds an extra layer of security to RDP logins, making it much more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access to your systems.
According to a recent report by Verizon, 81% of data breaches involve stolen or compromised credentials. MFA can help to prevent these attacks by requiring users to provide two or more factors of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code from their phone.
To implement MFA for RDP, you can use a variety of solutions, including:
- Azure Active Directory (AD) MFA: Azure AD MFA is a cloud-based MFA solution that is integrated with Windows Server and Remote Desktop Services. It supports a variety of authentication factors, including one-time codes from a mobile app, phone calls, and text messages.
- Third-party MFA solutions: There are several third-party MFA solutions available that can be used with RDP. These solutions typically offer a variety of authentication factors, as well as additional features such as risk-based authentication and adaptive authentication.
By deploying MFA solutions, organizations can bolster the security of their RDP servers and mitigate the inherent risks associated with pavssword-based authentication.
Securing RDP Server Connections with SSL/TLS
Securing Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) server connections with industry-standard encryption protocols, such as SSL/TLS, is essential in safeguarding the confidentiality and integrity of data transmitted during remote sessions.
To secure RDP server connections with SSL/TLS, you will need to:
Generate an SSL/TLS certificate for the RDP server:
- If you are using a self-signed certificate, you can generate one using the following command:
| openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout key.pem -out cert.pem -days 365 |
- If you are using a certificate from a trusted CA, you will need to follow the CA’s instructions for obtaining a certificate.
Configure the RDP server to use the SSL/TLS certificate:
- Open the Group Policy Management Console (gpmc.msc).
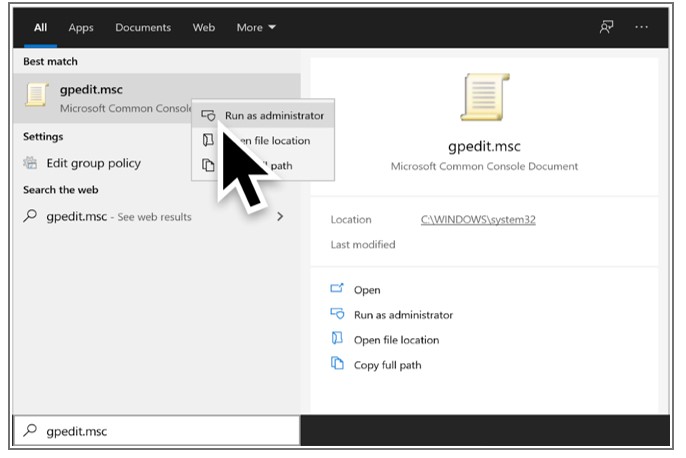
- Navigate to the following GPO section:
Computer Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Security
- Enable the following policy: Require the use of a specific security layer for remote (RDP) connections
- In the Options area, select the SSL security layer.
- Click OK to save your changes.
Configure the RDP client to require SSL/TLS encryption:
- Open the Remote Desktop Connection client.
- Click the Show Options link.
- In the Security section, select the Require TLS 1.2 encryption checkbox.
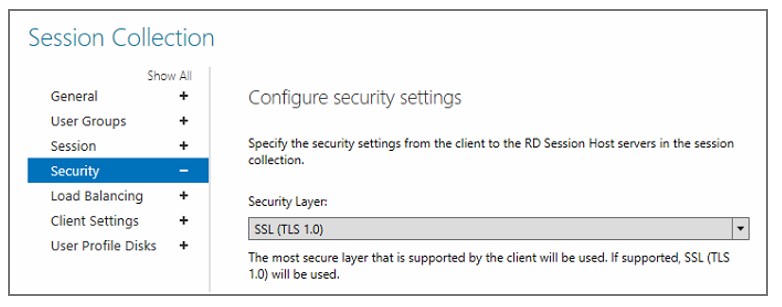
- Click Connect to connect to the RDP server.
Once you have completed these steps, your RDP server connections will be secured using SSL/TLS encryption. By integrating it into RDP server connections, organizations can mitigate the risk of data exposure and unauthorized access, enhancing the overall security posture of their remote access infrastructure.
RDP Server Security Tools and Software
A wide range of security tools and software solutions are available to assist organizations in enhancing the security of their RDP servers and mitigating potential risks and vulnerabilities. let’s highlight key security tools and software that can be leveraged to fortify the overall security posture of RDP servers, addressing various aspects of access control, monitoring, and threat detection.
- Remote Desktop Security Management Platforms: According to a recent survey by Gartner, 75% of organizations are using or plan to use a remote desktop security management platform in the next two years. Specialized security management platforms designed for RDP servers offer comprehensive capabilities for access control, user authentication, session monitoring, and policy enforcement. These platforms provide centralized management and visibility into RDP server environments, enabling organizations to implement granular security controls and monitor user activities effectively.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): IDPS solutions tailored for RDP server environments help in detecting and preventing unauthorized access attempts, anomalous behavior, and potential security threats. By deploying IDPS solutions, organizations can augment their ability to identify and respond to security incidents in real-time, enhancing the overall resilience of their RDP servers.
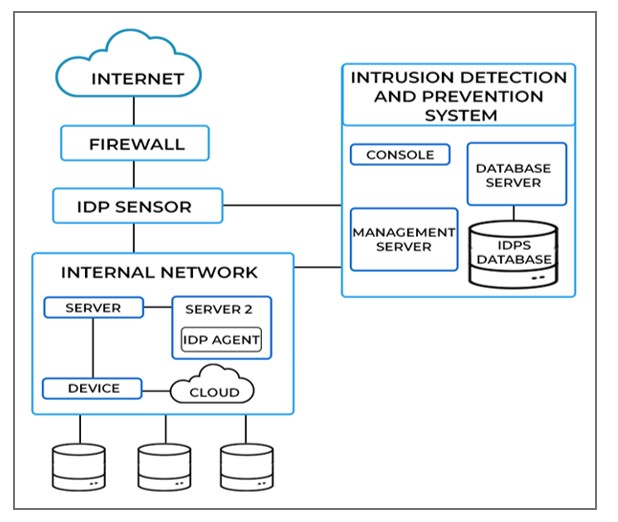
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Solutions: SIEM solutions offer advanced capabilities for aggregating, correlating, and analyzing security event data from RDP server environments, enabling organizations to gain actionable insights into potential security incidents and policy violations. By leveraging SIEM solutions, organizations can streamline their security monitoring and incident response processes, improving their overall security posture.
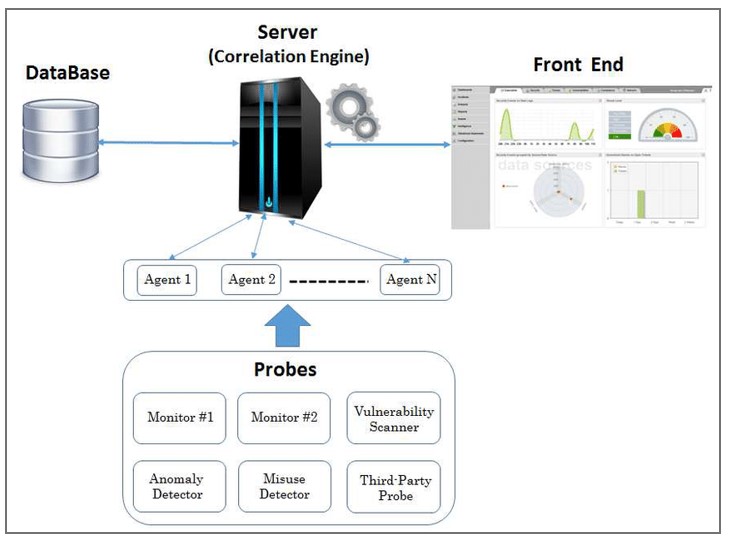
A classical architecture of an SIEM system.
- Endpoint Security Solutions: Endpoint security solutions that encompass anti-malware, host-based intrusion prevention, and device control features play a crucial role in securing RDP client devices and mitigating the risk of malware infections and unauthorized access attempts. By implementing robust endpoint security measures, organizations can fortify the security of RDP client endpoints and prevent potential threats from compromising RDP server access.
By leveraging these security tools and software solutions, organizations can bolster the overall security of their RDP servers and enhance their ability to detect, mitigate, and respond to potential security threats effectively.
Conclusion
Securing your RDP server is pivotal for safeguarding your network. By following these steps—strengthening passwords, enabling NLA, updating regularly, configuring firewalls, and considering extra layers like VPNs—you establish a robust defense. Remember, cybersecurity is a proactive effort. Regularly assess your server’s security, stay updated on the latest threats, and educate your team on secure practices. Implementing multi-factor authentication, securing connections with SSL/TLS, and leveraging security tools are also crucial steps toward fortifying your RDP server.
As technology advances, so do the tactics of cybercriminals. By investing in the security of your RDP server today, you’re not only protecting your data but also future-proofing your organization against evolving threats. Stay vigilant, stay secure.
Faqs
Q: Why is securing my RDP server important?
A: Securing your RDP server is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and protect sensitive data from potential cyber threats.
Q: What are essential security measures for an RDP server?
A: Implement strong passwords, enable network-level authentication, regularly update software, and configure firewalls to fortify your RDP server’s security.
Q: Can multi-factor authentication enhance RDP security?
A: Yes, enabling multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security, requiring users to verify their identity through a second method, such as a mobile app or text message.
Q: How often should I update my RDP server for security?
A: Regularly update your RDP server to patch vulnerabilities and ensure it stays resilient against emerging threats. Aim for timely application of security updates.
Q: Are there specific port configurations for a more secure RDP setup?
A: Yes, consider changing the default RDP port to reduce the risk of automated attacks. Using a non-standard port can enhance security by making it harder for attackers to locate and exploit your server.


Leave a Reply